Graduated from WSSG

It’s hard to believe that four months have passed without a trace. Looking back on my journey in the Advanced Design Games for Learning directed by Dr. Oprean, there are so many take-aways I would like to take with me as I continue to learn and study.
When I was a little boy, I needed to complete my assignments to get more time to play more games, however, in the Advanced Design Games for Learning course, I needed to play more games to complete my assignments…
What was the most important thing you learned this semester about game/simulation design?
On January 25, 2024, When I started my learning in the course of Advanced Design Games for Learning I wrote down my learning goals:
In this semester, I have three different leveled expectations for my learning in this course
The things I must master:
- All the assignments will be finished in time.
- All the projects will be finished as required.
- All the assigned content will be reviewed.
The things I want master:
- Equip more advanced game-based learning skills.
- Link the learning content to my publishable manuscripts.
The things I may master:
- Learn how to establish a high-standard game-based online course like Advanced Designing Games for Learning.
Now, looking back at the past, 4 months after the initial goal setting, how well did those goals go? First of all, I managed to cross the bottom line I set for myself. I completed most of my assignments on time (some were turned in later) and reviewed the required learning content regularly. I will continue to learn as I go along for the rest of my learning journey. I have now added more new advanced game-based learning skills to my teaching toolbox, such as learner personas, playtesting, teamwork, project management, and more. Another lucky thing, with the help of Dr. Oprean and Nicholas, I successfully submitted a manuscript on learning interest and game design to the Association for Educational Communication & Technology (AECT). So, what is the most important thing I have learned this semester about game/simulation design?
The answer is my deeper understanding of the relationship between learning and games. Games and learning, I now believe, are not in conflict; they can be mutually reinforcing when properly designed and organized. I always have a quote in my mind, “People do not learn from technology; they learn from thinking. When technologies can enhance students’ thinking, they should be used. Otherwise, they are probably no better than no technology.” This sentence was from David H. Jonassen, when he commented on the relationships between learning and technology during an interview(Simsek, 2012). When we use serious games to facilitate people’s learning, it falls under the category of technology. Therefore, designing more games that help players learn more smoothly, happily, meaningfully, and deeply is my current goal.
The course Advanced Design Games for Learning was a great example for me. During the learning process of this course, I often forgot whether I was learning or playing. I also often lost sight of the difference between games, serious games, simulation games, and simulations. When I dive in and indulge in a state of “flow”, the sheer joy of it can be equally successful and fulfilling. I thought, how could I make learning another kind of entertainment for learners? This is my new goal and the most important thing I have learned in this course.
What are some possible ways for me to achieve my new goal – to design more games that help players learn more smoothly, happily, meaningfully, and deeply?
Games can be used as a catalyst
Games could be used as a catalyst to stimulate and maintain the learners’ learning state and expand the attention span. When I am playing games to learn as a learner, the thing I look forward to the most is seeking more new ways or perspectives to observe what I am learning. For example, if I want to learn about the spatial relationship between the Earth and the Sun and other celestial bodies, I can choose to learn by reading books, or I can choose to learn by watching documentaries, or I can choose to play games. Space science games can give me the opportunity to maneuver a spaceship through the solar system and explore. This experience can give me a sense of freedom while playing the game. And the sense of freedom that the game brings can, ideally, make me avoid the unfamiliar vocabulary in books and the difficult voice intonations in documentaries – allowing me to avoid the difficulties or anxiety that exists in the traditional way of learning, and allowing me to regain my vigor. Next, based on the confidence I gained from playing space science games, I may be more interested in reading books and watching documentaries which have potential challenges for me to learn more about the universe.
Another trinity: a learner, a user and a player.
Who are your audiences? This is a very important question for those who prepare things for their audiences. Once, I attended a workshop at the Teaching for Learning Center. The workshop facilitator, Dr. Bethany Stone reminded me again that all the good instructors need to understand their audiences. While designing a serious game, the reminder is very meaningful. My understanding is beyond it.
When I worked as a science teacher, my primary audience was the learners in my classrooms and labs (students); when I worked as a private school administrator, my primary audience was the users (parents) at an information session to introduce our new school; when I worked as a serious game designer, my audience was virtually unchanged – students and parents – but my understanding of them shifted by this course. They are simultaneously learners, users, and players. Creating learner personas is an effective way for me to quickly understand my audience.
Loop and iteration
With a better understanding of the audience, building a game will be an iterative loop that involves a lot of “chicken or egg” dynamics. At this stage, don’t be afraid to start anywhere. Each new development will move the game forward in an interactive way. During this process, playtest reviews help me keep polishing the game to meet the audience’s expectations.
“The Rule of the Loop: The more times you test and improve your design, the better your game will be.” – Jesse Schell (The Art of Game Design: A Book of Lenses)
What are you most proud of from this semester?
One of the things I am most proud of this semester is the team project we completed as the ShowMeGeo studio. I am so proud of the ambition, imagination, and creativity of all the members of the team during our six-week game development marathon.
Where do good game ideas come from? Kultima concluded some points from the interviews that, “Good ideas were seen as inspiring for others to immediately build on top of them. It was seen as beneficial when a description gave enough information for others to imagine the idea, but enough space for them to develop it further. The bouncing of ideas would expose that quality of an idea.” (Kultima, n.d.)

The team design process was not as fluent and smooth as I imagined. Each step of the development contained some challenges and chances at the same time. But the real value of learning was harvested during this complicated process.
There was one example of the collaboration value during the team-work process. During a weekend brainstorming session inspired by one team member, Maureen, I developed a game idea while cycling on the MKT trail in Columbia, MO. This idea was influenced by geographic facts displayed on the trail, leading to the creation of our game “CoMo Valley,” which incorporates different spaces and historical periods. Apparently, I could not have this serendipity without team members’ help.
When we were in the “Design Loop”, We often debated which component should be introduced first: game mechanics, instructional objectives, assessment plans, or storyboard design? There is no definitive answer, as the ideal approach may vary from one game studio to another.
I confirmed this assumption during a guest lecture with Greg Marlow, who has extensive experience in both the game industry and academic settings focused on game design. The design process is inherently iterative—meaning the more times you test and refine your design, the better your game will become (Schell, 2019) . This also aligns with Dr. Oprean’s initial introduction to the course, where we embraced the concept of being in a continuous loop of development and improvement.
One key realization I had during our game development process is the importance of continually revisiting the problem description. I found myself rereading it numerous times to ensure that our design stayed aligned with the initial goals and objectives. This constant reference helped keep our project on the right track, ensuring that every element of the game design directly addressed the core issues we set out to solve. It served as a crucial checkpoint that guided our development decisions and helped maintain a clear focus throughout the iterative design process.
Research play persona,Given my background in geography and firsthand observations of secondary school students who pursue it as a major or research direction, I am well-equipped to assist my colleague Maureen in developing the learner persona, with a particular focus on those younger than college age. I am eager to contribute to the descriptions of our learner personas, particularly for high school and middle school students, leveraging real-world examples and experiences to ensure our game design effectively resonates with and educates this demographic.
Teamwork is the dream work,here is the pitch slide of our game, Echoes of Lalibela Pitch Slideshow – Google Slides
What if anything will be most helpful for you moving forward (either with games for learning or moving away from it)?
While proceeding with my further learning and research, there are some helpful tips:
- When you encounter “difficult” problems, try to transform them into “complex” problems.
Based on my observations, most of the puzzles that I find unsolvable can be transformed into complex problems that contain many sub-problems. As each problem is eventually solved, the original problem disappears. If someone asked me to create a game for people to learn geography without detailed instructions on how to create learner characters, how to integrate the instructional objectives with the game mechanics, and how to conduct playtests, I would likely be lost. Charismatic teaching is the work of turning difficult problems into complex ones, and then step by step making them solvable.
- Systematic design
Systematic thinking is another powerful tool for me. This systematic thinking will be very useful for my future design work. I would like to design learning games while considering goals, content, feedback, manipulation, and assessment.
- Keep moving forward and iterating
If you have some concerns or questions, a better solution might be to jump to the next step and do something else that you might be able to do, rather than stopping there and just focusing on the problem. Sometimes the key to unlocking a locked door is not near the door, but far away from it. You may find the solution far away from the problem that is holding you back.
Read MorePlaytest Review

A cartoonish, animated scene in the style of modern western animation, with vivid colors, depicting a game tester conductor in a whimsical, professional attire, interviewing a college-aged game tester. (Created by Yupei and ChatGPT)
Initially, I wanted to invite one of my previous students to do the playtest. However, due to his busy schedule, we had to cancel the appointment. I changed to ask my family members to be the playtesters. One of them accepted; let’s call her participant A. Participant A, older than our targeted audience and with no direct connection to geographic research areas, is interested in playing more games and learning about geography.
Due to the different time zones we are living in, I used the asynchronous way to do the playtest. I sent the game to participant A at 10 am on April 27, Saturday (CST) and used the survey question to make an interview with participant A to collect her feedback to the game at around 10 pm on April 28, Sunday (CST).
For the user’s convenience, I used the survey questions to interview participant A instead of asking her to input the written feedback on the google form. After the interview, I transformed her feedback into survey data on the Google form.
Participant A was not familiar with the game engine and game platforms like itch.io. I used some time to introduce her to how to play the game.
Lessons Learned
- Time management
I lost my initial game tester due to the very limited time I gave to him. People may have temporal businesses to do and issues to tackle outside of the schedule. Next round, I hope I can leave more time for the game tester to do the test.
- Flexible options
Due to the variability of the game testers, the more different available test models they can choose, the more feedback we can get. The synchronous and asynchronous testing consideration was a great one in the game test. I would like to keep more flexible options to the testers in the future.
- Detailed instructions
Potential testers may not be familiar with our game; detailed instructions with helpful tips can enable them to quickly understand the game’s background, the rules, and start playtesting. We designed a brief introduction to the game background and the play rules to share with the testers which helped them emerge in the game faster. This helpful experience will be kept in the future.
- Diverse participants
Diverse participants may provide feedback on aspects of the game that the designers have not noticed. Originally I wanted to invite a participant with a background related to Geographic and owns more game experience to do the test to collect feedback about graphics elements in the game. The new participant with no direct connection with Geographic research and with limited game experience didn’t focus on the educational and game design elements, but she shared an unexpected view to the game musical and graphic settings, which were also vital for a successful educational game.
Suggested Design Improvements:
The general idea and design of the game were attractive and interesting. It would be better with more game mechanics and content. It would also be more interesting to add music and audio elements.
I want to suggest to the studio members to add more audio and graphic assets in the game, keep polishing the game narrative and design more game mechanics to show more educational content.
Appendix:
- Game Link:
Echos Of Lalibela by RRstrauss (itch.io) - Questionnaire:
Post-Playtesting Questionnaire – Google Forms - Survey Results (team work):
Demographic and Response information for 7 participants
Administered via Google Form
How do you identify?
Male 42.9%
Female 42.9%
Non-Binary 14.3%
How old are you?
19-24 57.1%
25+ 42.9%
How often do you play games?
Weekly 42.9%
Daily 14.3%
2-3x/week 14.3%
Less freq. 28.6%
Monthly 0%
What are 2-3 of your favorite games?
1. Slime Rancher, Stardew Valley, Terraria
2. D and D, Pente, Spirit Island
3. Legend of Zelda (All of them), Spirit Island, Subnautica
4. Hades, Assassins Creed Odyssey, KOTOR
5. Borderlands, Dwarf Fortress, COD
6. Ludo, Temple Run, Subway Surfers
7. Super Mario, Tetris
What are 2-3 of your least favorite games?
1. Risk, Chess (sorry)
2. Hop Scotch, Marbes, Tiddliwinks
3. I forgot because I don’t like them, and I don’t dislike them enough to remember
4. Gotham Knights, COD MW2
5. Tropico 6, Civ 6
6. NA
7. Some games with blood and violence
Have you ever played an educational game?
Yes 71.4%
No 28.6%
Have you ever taken a Geography class?
Yes 85.7%
No 14.3%
Are you familiar with professions associated with Geography degrees?
Yes 57.1%
No 42.9%
First Impressions of the Game
What are the first three words that come to mind after playing the game?
1. Scott, green, dice?
2. Incomplete, simple, potential
3. Squares, Path, Movement
4. Interesting, potential, engaging
5. Confusing, cool idea, potential
6. Educational to kids, Fun to play
7. Interesting, simple, narrative
Would you play this game again?
1 = No, 5 = Yes
2 57.1%
3 28.6%
5 14.3%
(Optional) Why or Why not?
1. More of a concept project than a repeatable experience
2. Can’t tell – there isn’t enough of it for me to have an opinion
3. As is, it’s not prepared enough to “Play”. The most basic elements of a game only partially exist.
4. I would play if the game were more playable.
5. It’s interesting but need to add on more features to make children attract
6. I would like to play it again if there was more stuff to explore
Would you like to learn more about this game?
1 = No, 5 = Yes
3 16.7%
4 33.3%
5 50%
(Optional) Why or Why not?
1. Looks like a neat concept and I would enjoy seeing it go further, it touched on ideas that would be interesting to see in a deeper game.
2. I would if this actually becomes an educational game
3. It’s game.
Were the directions clear?
1 = No, 5 = Yes
1 28.6%
2 28.6%
3 14.3%
4 28.6%
(Optional) Why or Why not?
1. Hard to remember what was expected, did not know how to move buildings, important details felt lost in character text
2. The icons were not clearly labeled. The directions should have remained visible on the playing page. No idea what the green squiggles were, where the ‘sacred trees’ were, et cetera.
3. Where were the directions?
4. Directions were unclear as to how to interact with the world and complete objectives.
Was the story interesting?
1 = No, 5 = Yes
2 42.9%
3 28.6%
4 28.6%
(Optional) Why or Why not?
1. There wasn’t much story that I saw? I think the character dialogue was most of the story building and there wasn’t much to supplement outside of character interactions
2. What story? There was a scenario that had potential, but not a story.
3. It didn’t feel particularly connected to the mechanics.
4. There was very little story, and what there was seemed aimed towards children
Were the controls easy to use?
1 = No, 5 = Yes
2 14.3%
4 57.1%
5 28.6%
(Optional) Why or Why not?
1. Controls were easy but I got confused about the parameters for where I could place buildings
2. The controls were arrow only – sure, easy to use.
3. I was using a wonky keyboard and trackpad. I did find it odd that I could move everywhere freely.
4. Had trouble controlling without a mouse, very sensitive.
Were you able to “win” the game?
Yes 71.4%
No 28.6%
Everything these six weeks taught me
“The Rule of the Loop: The more times you test and improve your design, the better your game will be.” – Jesse Schell (The Art of Game Design: A Book of Lenses)
I think I now have a deeper understanding of the above sentence by Jesse Schell pointing out the nature of design. I would like to share my thoughts on this quote and use the last six weeks of design loop to look back my personal work in the team and reflect on what these six weeks has taught me.
Team Formation
Starting with the team’s name, Maureen, Nicholas, Rachael, Joshua, and I got together to name our game design team. We had quite a few nice options, like Gaia Games Studio, GeoForce Studio, and Terra Learner Labs. Luckily, my proposed team name “ShowMeGeo Studio” was selected. It shows our identity, aligns with client expectations, and reflects our game’s goal—to introduce Geological majors. I am proud to be the creator of the team’s name.
Play More Games Before Designing One
Before we started designing the game, Dr. Oprean asked us to find, play, and share games related to geological majors. Through this exploration, I noticed many games were related to maps, possibly because maps are easier to design into games or simulations.
With the insights gained from playing games shared by other team members, I confirmed my assumption about the common use of maps in geological games. This led us to ponder: What other possibilities could we explore in geological game design? With this question in mind, we began researching our audience.
Understanding the audience is crucial for guiding our next steps in game development. By gaining a deeper insight into the interests, educational backgrounds, and gameplay preferences of our target players, we can tailor our game to better meet their needs and enhance their learning experience.
Researching Learner Persona
During the persona research phase, I drew upon my extensive experience as a secondary school science teacher to contribute to our team’s creation of learner personas. With 16 years of teaching in K-12 schools, I have observed many students choosing geography or related majors as they advance to college or graduate school. Recently, one of my former students, who is now attending the University of Nevada, secured a NASA research grant for his groundbreaking black hole research. Zhang, who was once just a curious young student in my science class in Beijing, China, is an example of the type of student who can significantly inform the development of our learner personas.
Given my background in geography and firsthand observations of secondary school students who pursue it as a major or research direction, I am well-equipped to assist my colleague Maureen in developing the learner persona, with a particular focus on those younger than college age. I am eager to contribute to the descriptions of our learner personas, particularly for high school and middle school students, leveraging real-world examples and experiences to ensure our game design effectively resonates with and educates this demographic.
Game Design
Starting from last semester, in Dr. Oprean’s course “Design Games for Learning”—the one before the current advanced course I am taking—I have been pondering the differences between games, movies, instructional design, and cooking. These thoughts frequently emerged in my mind, sparked by the many similarities between these disciplines. While writing a blog to review the past six weeks, these thoughts visited me again.
In my opinion, game design closely resembles movie design, instructional design, and even cooking. Why? Because all involve preparation: a game blueprint, screenwriting, a lesson plan, or a cooking procedure. The clients of the game, the viewers of the movie, the students in a class, and the tasters for a dish are the targets for these designs. All need interactive improvements if the creators wish to present the best to the end user.
You can find lovers of good food, elegant instructions, impressive movies, and playful games everywhere. Additionally, I think good games can also be attractive movies, informative instructions, and high-quality “spirit food,” especially in the case of story games like those ShowMeGeo Studio has been designing.
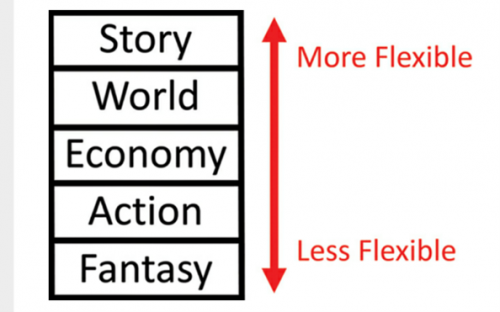
Schell, J. (2019). The Art of Game Design: A Book of Lenses, Third Edition (3rd edition). A K Peters/CRC Press. )
Jesse Schell used a figure (Schell, 2019) to illustrate the five important elements that comprise story games: Story, World, Economy, Action, and Fantasy. From this figure, I could confirm my imagination about the relationships between games, movies, instruction, and food once again. Because again, games, movies, teaching, and food can all contain the same five elements, and those elements can be improved upon by the designer.
For the importance of the story design in a game, Schell (2019) pointed out, “ When developing a game with a compelling story, it can be very tempting to start not by designing a game but by writing your story.” Now, let me focus on the story design.
Game Storming
Where do good game ideas come from? Kultima concluded some points from the interviews that, “Good ideas were seen as inspiring for others to immediately build on top of them. It was seen as beneficial when a description gave enough information for other to imagine the idea, but enough space for them to develop it further. The bouncing of ideas would expose that quality of an idea.” (Kultima, n.d.) During a weekend brainstorming session inspired by Maureen, I developed a game idea while cycling on the MKT trail in Columbia, MO. This idea was influenced by geographic facts displayed on the trail (figure 3), leading to the creation of our game “CoMo Valley,” which incorporates different spaces and historical periods.

The Design Loop
When the five of us began sharing our specific ideas on a shared Google Doc, we quickly encountered a “chicken or egg” dynamic. This dynamic persisted in the following weeks as we developed the Storyboard, Objective Mapping, Assessment Plan, and the Concept Testing Report. We often debated which component should be introduced first: game mechanics, instructional objectives, assessment plans, or storyboard design? There is no definitive answer, as the ideal approach may vary from one game studio to another.
I confirmed this assumption during a guest lecture with Greg Marlow, who has extensive experience in both the game industry and academic settings focused on game design. The design process is inherently iterative—meaning the more times you test and refine your design, the better your game will become (Schell, 2019) . This also aligns with Dr. Oprean’s initial introduction to the course, where we embraced the concept of being in a continuous loop of development and improvement.
One key realization I had during our game development process is the importance of continually revisiting the problem description. I found myself rereading it numerous times to ensure that our design stayed aligned with the initial goals and objectives. This constant reference helped keep our project on the right track, ensuring that every element of the game design directly addressed the core issues we set out to solve. It served as a crucial checkpoint that guided our development decisions and helped maintain a clear focus throughout the iterative design process.
Problem Description
- There has been a steady decline in Geography majors over the years despite the real-world need for keeping the long-standing discipline alive. To better understand the problem, you can read a bit more on the decline here.
- Very few games and simulation solution exist to engage in the practice of Geography.
- Geography is a multi-faceted discipline with very diverse areas of practice, many of which are often confused with other discipline in Environmental Sciences and GeoScience.
- Geography in practice differs from what is taught in K-12 classrooms (K-12 classrooms focus on facts-based information where Geographers synthesize and draw meaning from human and environment interactions).
During this development phase, Dr. Soren Larsen shared his expectations for the game, emphasizing the importance of enhancing students’ abilities to analyze spatial patterns. The challenge was to design a game that not only helps novice learners understand the role of geographers but also trains students majoring in geography to analyze spatial patterns on thematic maps effectively.
To address this dual need, I suggested a multi-level design approach. This strategy allows us to cater to both novice and professional learners within the same game environment. By implementing different levels of complexity and challenge, we can ensure that our game is accessible yet sufficiently challenging to engage and educate players at various stages of their educational journey. This approach aims to provide a seamless learning curve that enhances the educational value of the game for all users.
Reflecting on My Process
As an experienced secondary teacher, I brought a lot of first-hand educational experience to our design process. Despite challenges in communication due to language barriers, I learned the importance of patience and persistence in game design.
New Content
The past six weeks have taught me the significant impact of patience in designing games, and the immense effort required to create games like “Stardew Valley” as an individual.
This process has been a valuable part of my learning and growth as a game designer, helping me to understand the intricate relationship between different creative processes and the importance of iterative design in game development.
References
Forming a Learner-Player Persona
I attended a workshop at the Teaching for Learning Center. Once again, I was reminded by the host of the workshop (slides) Dr. Bethany Stone that all the good lecturers need to understand their audiences. While designing a serious game, the reminder is still meaningful. ShowMeGeo Studios memembers have been working on designing a learner-player personna to develop a serious game to introduce more audience what the geographers do. Dr. Opren encouraged us to design the persona from three different perspectives: a learner, a user and a player.
Part 1: Gather Some Information for creating a learner persona
As a learner, the most important thing, while I play games for learning, is providing me with a new way or new angle to observe the learning content. For example, I can learn the special relationships between the planet earth and sun and other celestial bodies according to read books and watch documentary films. But the game may provide me a chance to manipulate a spaceship to travel through our solar system to explore them. For the most valuable entertainment I would like to enjoy while playing games, is a feeling of freedom. The freedom bring by the game should let me forget the difficulties in my real life and help me forget bitterness or anxiety for a while, which help me refresh. When I use games and simulations as learning tools, my highest expectations is to extend my attention span to focus on practicing or learning.
Source of the information: I have asked three secondary school students about their preferences while playing games. I interviewed them and record their responses.
Types of information I collected: verbal descriptions.
Part 2: Analyze my Findings for creating a learner persona
When I taught science courses in my former school, I used game-based learning as a very important teaching strategy. From my experience, I could understand learners’ preferences when they engaged in the learning games. So, I conducted virtual interviews with three of my former students who, during their middle or high school years, chose Geography as their major in college. As their former science teacher and homeroom teacher, I not only maintain close connections with them but also have a deep understanding of their personalities and experiences. Please note that these three students represent a larger group who majored in Geography, embodying the most common traits of those passionate about the subject.
Based on my virtual interviews with these former students, I have summarized my findings below. Additionally, if time permits, I would like to share and discuss these findings with the real persons to refine and enhance my understanding.
| Participant 1 | Participant 2 | Participant 3 | |
| Name | Zhang | Qin | Zhu |
| Bio | G7 student in middle school. GPA is in top 20% of his class. Interested in observing starry night. | Freshman in high school. GPA is in top 40% of her class. Interested in investigating the stories back of the hills and rivers. | Senior in high school. GPA is in top 60% of his class. Interested in traveling around the world. |
| Age | 13 | 15 | 17 |
| Gender | Male | Female | Male |
| What is important to you when you play games for learning? | How can I learn fast and better? | Not too hard and complicated. | Help me understand the learning content. |
| What is important to you when you play games for entertainment? | I want to have more joy. | Peaceful and beautiful. | Give me a real experience feeling. |
| What is important to you regarding user experience and usability with learning games as learning tools? | Can it help me tackle learning difficulties? | Use less time and learn more. | I want it can give me possibilities to design my games to learn the knowledge. |
Part 3: Reflect on my Data Collection Process
I would like to express my sincere thanks to Maureen for providing a well-structured learner persona template. Following our discussions on Canvas and during our online meeting, we have decided to merge her college student learner persona with my high school student persona. Narrowing the focus from broad to specific presents a challenge, as does expanding your focus in diverse directions. Drawing on the insights gained from virtual interviews with my former students, I am proposing a secondary school learner persona utilizing Maureen’s template. The referenced articles are: How to Use Learner Personas to Understand Your Audience (growthengineering.co.uk)And How to Develop Learner Personas for Effective Training (td.org)
A new learner persona (high-school student) created by me
Name: Danny
Bio:
Age: 15 Freshman
in high school. GPA is in top 50% of his class. From a mid-size city,
studying in a public high school, interested in travelling
Race: mixed race
Gender: Male
Motivation: stories enthusiast
Key character
traits: curious energetic, positive,
considers himself a Creative
Key learning
type: kinesthetic learner (learns by
doing), Visual learner, naturalistic learner
Key challenges toward
learning: does not like math, has trouble
concentrating during lectures, requires highly structured instructions, wants
all classes to be goal oriented, difficulty understanding scientific concepts.
Games: Role-Playing-Games and flight simulation games.
A learner persona (a college student) created by Maureen
Name: Sue Learner (she/her)
Bio: College Freshman, currently Undecided.
Graduated in top 25% of her high school class. From a small, rural
community and attending a large public university. Follows van life
influencers and is interested in building a tiny house.
Age: 18
Race: mixed race
Gender: female
Motivation: Wants a job in “sustainability,” financial stability
Key character
traits: excited, self-motivated,
positive, considers herself a Creative
Key learning
type: kinesthetic learner (learns by
doing)
Key challenges toward
learning: does not like math, has trouble
concentrating during lectures, requires highly structured instructions, wants
all classes to be goal oriented.
Games: Enjoys Stardew Valley, Animal Crossing, and
Breath of the Wild, has a Twitch stream with 250 followers. Prefers solo
games, but likes to chat with her followers while playing.
Part 4: The combination learner persona
Name: Kayla S. Learner (she/her)
Bio: Age: 17, Senior in high school with a GPA in the top 40% of her class. From a mid-size city and interested in sustainability, particularly in the context of travel and building spaces such as tiny houses.
Race: Mixed race
Gender: Female
Motivation: Passionate about stories telling, sustainability, and financial stability. Aims to work in a field that combines their creative interests with environmental consciousness.
Key Character Traits: Curious, energetic, excited, self-motivated, positive, and highly creative.
Key Learning Type: Kinesthetic learner (learns by doing), visual learner, and naturalistic learner.
Key Challenges Toward Learning: Struggles with math and has difficulty concentrating during lectures, needs highly structured instructions, prefers goal-oriented classes, and sometimes finds scientific concepts challenging.
Games: Enjoys a variety of games, including role-playing games, flight simulation, Stardew Valley, Animal Crossing, and Breath of the Wild. They have a moderate following on Twitch where they engage with followers while playing mainly solo games, but also enjoy the social interaction that comes with streaming.
The challenges I encountered for forming information into a persona were include which the key words I should select can on behalf of the main traits of the interviewees? How can I use a simple but accurate way to describe the learner personal? Finally, I thought the current process for me was to get a quick and dirty persona as a scratch to continue the following steps. I should focus on the main traits of the users.
Read MoreResearching Learner Persona
I will use this blog entry to share my learner persona creation, as well as the reflection of the whole creation process.
Part 1: Gather Some Information
As a learner, the most important thing while I playing games for learning is providing me a new way or new angle to observe the learning content. For example, I can learn the special relationships between planet earth and sun and other celestial bodies according to read books and watch documentary films. But the game may provide me a chance to manipulate a spaceship to travel through our solar system to explore them. For the most valuable entertainment I would like to enjoy while playing games, is a feeling of freedom. The freedom bring by the game should let me forget the difficulties in my real life and help me forget bitterness or anxiety for a while, which help me refresh. When I use games and simulations as learning tools, my highest expectations is to extend my attention span to focus on practicing or learning.
Source of the information: I have asked three secondary school students about their preferences while playing games. I interviewed them and record their responses.
Types of information I collected: verbal descriptions.
Part 2: Analyze my Findings
When I taught science courses in my former school, I used game-based learning as a very important teaching strategy. From my experience, I could understand learners’ preferences when they engaged in the learning games. So, I conducted virtual interviews with three of my former students who, during their middle or high school years, chose Geography as their major in college. As their former science teacher and homeroom teacher, I not only maintain close connections with them but also have a deep understanding of their personalities and experiences. Please note that these three students represent a larger group who majored in Geography, embodying the most common traits of those passionate about the subject.
Based on my virtual interviews with these former students, I have summarized my findings below. Additionally, if time permits, I would like to share and discuss these findings with the real persons to refine and enhance my understanding.
| Participant 1 | Participant 2 | Participant 3 | |
| Name | Zhang | Qin | Zhu |
| Bio | G7 student in middle school. GPA is in top 20% of his class. Interested in observing starry night. | Freshman in high school. GPA is in top 40% of her class. Interested in investigating the stories back of the hills and rivers. | Senior in high school. GPA is in top 60% of his class. Interested in traveling around the world. |
| Age | 13 | 15 | 17 |
| Gender | Male | Female | Male |
| What is important to you when you play games for learning? | How can I learn fast and better? | Not too hard and complicated. | Help me understand the learning content. |
| What is important to you when you play games for entertainment? | I want to have more joy. | Peaceful and beautiful. | Give me a real experience feeling. |
| What is important to you regarding user experience and usability with learning games as learning tools? | Can it help me tackle learning difficulties? | Use less time and learn more. | I want it can give me possibilities to design my games to learn the knowledge. |
Part 3: Reflect on my Data Collection Process
I would like to express my sincere thanks to Maureen for providing a well-structured learner persona template. Following our discussions on Canvas and during our online meeting, we have decided to merge her college student learner persona with my high school student persona. Narrowing the focus from broad to specific presents a challenge, as does expanding your focus in diverse directions. Drawing on the insights gained from virtual interviews with my former students, I am proposing a secondary school learner persona utilizing Maureen’s template. The referenced articles are: How to Use Learner Personas to Understand Your Audience (growthengineering.co.uk)And How to Develop Learner Personas for Effective Training (td.org)
A new learner persona (high-school student) created by me
Name: Danny
Bio:
Age: 15 Freshman
in high school. GPA is in top 50% of his class. From a mid-size city,
studying in a public high school, interested in travelling
Race: mixed race
Gender: Male
Motivation: stories enthusiast
Key character
traits: curious energetic, positive,
considers himself a Creative
Key learning
type: kinesthetic learner (learns by
doing), Visual learner, naturalistic learner
Key challenges toward
learning: does not like math, has trouble
concentrating during lectures, requires highly structured instructions, wants
all classes to be goal oriented, difficulty understanding scientific concepts.
Games: Role-Playing-Games and flight simulation games.
A learner persona (a college student) created by Maureen
Name: Sue Learner (she/her)
Bio: College Freshman, currently Undecided.
Graduated in top 25% of her high school class. From a small, rural
community and attending a large public university. Follows van life
influencers and is interested in building a tiny house.
Age: 18
Race: mixed race
Gender: female
Motivation: Wants a job in “sustainability,” financial stability
Key character
traits: excited, self-motivated,
positive, considers herself a Creative
Key learning
type: kinesthetic learner (learns by
doing)
Key challenges toward
learning: does not like math, has trouble
concentrating during lectures, requires highly structured instructions, wants
all classes to be goal oriented.
Games: Enjoys Stardew Valley, Animal Crossing, and
Breath of the Wild, has a Twitch stream with 250 followers. Prefers solo
games, but likes to chat with her followers while playing.
The combination learner persona
Name: Danielle Learner (she/her)
Bio: Age: 17, Senior in high school with a GPA in the top 40% of their class. From a mid-size city and interested in sustainability, particularly in the context of travel and building spaces such as tiny houses.
Race: Mixed race
Gender: Female
Motivation: Passionate about stories telling, sustainability, and financial stability. Aims to work in a field that combines their creative interests with environmental consciousness.
Key Character Traits: Curious, energetic, excited, self-motivated, positive, and highly creative.
Key Learning Type: Kinesthetic learner (learns by doing), visual learner, and naturalistic learner.
Key Challenges Toward Learning: Struggles with math and has difficulty concentrating during lectures, needs highly structured instructions, prefers goal-oriented classes, and sometimes finds scientific concepts challenging.
Games: Enjoys a variety of games, including role-playing games, flight simulation, Stardew Valley, Animal Crossing, and Breath of the Wild. They have a moderate following on Twitch where they engage with followers while playing mainly solo games, but also enjoy the social interaction that comes with streaming.
The challenges I encountered for forming information into a persona were include which the key words I should select can on behalf of the main traits of the interviewees? How can I use a simple but accurate way to describe the learner personal? Finally, I thought the current process for me was to get a quick and dirty persona as a scratch to continue the following steps. I should focus on the main traits of the users.
If I had to do this again, I wish to collect more experienced teachers’ feedbacks about their students who eventually chose Geography as college majors. I would like to design a survey to collect the persona information both from teachers and students.
Read More